The surprise supplement that transformed my thinning hair
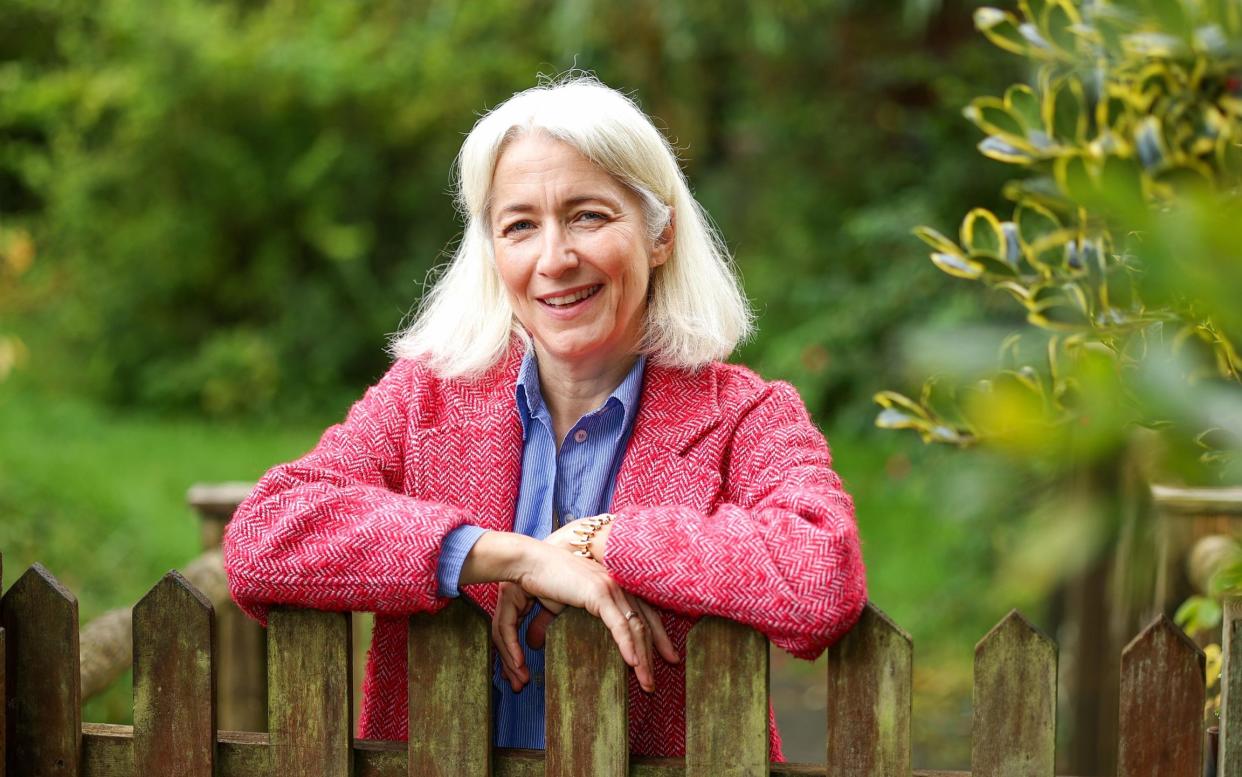

“You are a good candidate for a hair transplant,” said the surgeon, drawing a dotted line onto my temple to show where he’d put the new hair. I felt a flush of relief: something could actually be done about my hair loss. So desperate was I, here I was considering borrowing £6,000 for the procedure, the same one Wayne Rooney reportedly had. A strip of hair and skin is incised from the back of your head; you are only a “good candidate” if you have enough hair there. The surgeon tweezes out the hairs from the follicles and replants them, little rows of saplings growing on formerly barren land.
I first noticed my hair loss in my mid-40s, although it likely started at the very beginning of perimenopause, when I was around 40. The hair around my face shortened, as if I’d had layers cut. It got thinner. When I noticed my temples were becoming sparse, I changed to a middle parting to cover them.
The exact root of female pattern hair loss (FPHL) remains unknown but it’s likely that follicles’ sensitivity to changes in oestrogen during perimenopause is key. “Oestrogen is a hair-friendly hormone, helping to keep hair in the anagen [growing] phase,” says trichologist Anabel Kingsley, brand president of Philip Kingsley clinics.
During perimenopause, while oestrogen fluctuates, progesterone drops. This left my follicles vulnerable to the effects of androgens, specifically one called DHT (dihydrotestosterone), which slows and stunts hair growth. “This affects both the texture and the density of the hair,” says hair scientist Amy Meshkati, founder of the Meshkati Clinic.
By the time I saw the hair transplant surgeon, I had stage 3 hair loss (out of a possible 5).
Hair loss can be devastating
Research shows women are psychologically hit harder by hair loss than men, more likely to feel socially anxious, even socially phobic. “Women, unlike men, feel the need to apologise for minding,” says Kingsley. They say, “I’m not a vain person”, or “I’m sorry if I seem silly”.
The changes in my hair were nothing compared to someone who’s lost all or most of their hair, but they still stung. US star Ricki Lake wrote on social media about her hair loss in January 2020. At first, she said, she told almost no one “the deep pain and trauma” of her experience, that it left her feeling “suicidal”.
Hair matters because it screams health, youth, femininity, fertility and “hotness”. That’s why the hair transplant market, worth $5 billion in 2022 – estimated to reach $23 billion by 2030 – has an increasing share of women having the op.
When you’re losing your hair, you become acutely conscious of it. Every blow-dry left a thin layer of hairs on the carpet, as if a white long-haired cat had been sitting underneath me. Every hair I picked off my cardigan, yoga mat or car seat gave me a jolt, because it felt like another tiny step closer to baldness. I would eye Claudia Winkleman’s thick, lush fringe and mane on The Traitors, and think, why me?
In her memoir Giving Up The Ghost, Hilary Mantel wrote: “You come to this place mid-life. You don’t know how you got here but suddenly you’re staring 50 in the face.” I was staring 50 in the hair. I could deal with wrinkles, eye bags, mousey greying. But being on a summer holiday and a gust of wind blowing through my hair exposing my balding patches? That, I couldn’t.
Panicking, I did the opposite of what you should do. With so many products and treatments available, I must have wasted over £500, on ineffective shampoos, supplements and lotions with big promises, bought late at night on Instagram. Here’s what I tried, what helped my hair loss, and what didn’t.
Hormone treatment
“In midlife, perimenopausal hormonal shifts can trigger or worsen changes in hair size,” says Kingsley. Hair on the top of the head can be most obvious along the parting, on the crown and also on the temples. It can get progressively skinnier in diameter and shorter in length, a process called miniaturisation, until they become wispy then disappear. Follicles can stop producing hair altogether, although this is more common in men.
“The sooner you treat the issue, the stronger the result,” says Meshkati. “Once the follicle is lost, you can never grow back the hair, but you can control hair loss before that. Hair loss rarely reverts to normal without profound treatment. You also need to supervise and adjust hormonal balance.”
I took a DUTCH hormone test with nutritionist Pippa Campbell, where you pee on little blotting papers over 24 hours. It showed my progesterone was too low but, like two thirds of women with hair loss, my androgens weren’t high. There is a drug option for those with high androgens: spironolactone tablets, a common diuretic that’s often prescribed off-label for hair loss too.
Minoxidil
A trichologist I saw suggested minoxidil lotion, the only UK-licensed medication for female hair loss, available at chemists. Originally a drug to treat blood pressure, minoxidil works by increasing blood flow by creating new blood vessels to follicles.
The most common brand of minoxidil is Rogaine. Minoxidil works for 60 to 70 per cent of women. Sadly, I wasn’t one of them.
“Minoxidil works best when it’s combined with other ingredients,” says Kingsley. The Philip Kingsley clinic makes two variations of this. One contains melatonin which is known as “the sleepy hormone”, but in follicles it works as an antioxidant to fight the inflammation which adds to hair loss. I use the one that’s been dubbed hair HRT because it contains oestrogen and progesterone, and using this has definitely helped me regrow some hair. For people who don’t get on with minoxidil, the clinic recommends adenosine, which is said to stimulate hair growth.
I had an online consultation with Harklinikken, manufacturers of the products that Ricki Lake used to regrow her hair, but it felt more like a sales pitch.
Scalp inflammation has also been linked to hair loss. I buy Plantmade products, a range made from natural oils including rosemary oil, which in one study got similar results to minoxidil. I’ve found it calms any scalp soreness, and I have seen newer short, dark hairs while using it.

TrichoTest
A year ago, I had a DNA test, TrichoTest, that analyses which of a range of medicines and natural substances might work for you. My result was positive for oestrogen but also for latanoprost (originally a treatment for glaucoma, now used cosmetically as a lash lengthener). Naturally you need a lot more for hair than for lashes, and unfortunately latanoprost is expensive. I order mine via Grow Back, pharmacists who specialise in hair loss medication. Results seem very promising but like minoxidil lotion, it only works while you’re taking it.
I have also started trying my own, free circulation-boosting treatments: head massages and rinsing my hair with cold water, as Meshkati recommends.
Follicle regeneration treatments
By this stage I’ll try anything with a modicum of science behind it. I had some sessions of Platelet-Rich Plasma Injections (PRP) where your blood is taken, the growth factors are extracted from it, and needled back into the scalp.
This slowed the loss but the results didn’t last for me.
I’m starting a six-week course of Calecim, an ointment which sounds even stranger, containing “proteins and growth factors derived from umbilical cord lining of New Zealand red deer,” says Kelly Morrell of Scalp Confidential, an aesthetic practitioner who specialises in hair loss. But I’m hopeful. “As long as the follicle is still there, Calecim can be a game-changer,” says Morrell. Like all hair treatments, I’ll have to wait for results, at least six weeks. “Hair is much slower than skin to show change,” says Dr Thivi Marupatthu, the UK’s only nutritionist and dermatologist, and author of SkinFood.
Diet & supplementation
Hair is pretty low on the body’s maintenance list, so it’s one of the first things to go when diet isn’t good. “Disordered eating or weight loss can lead to hair shedding,” says Marupatthu. She’s seen clients with hair loss after taking Ozempic, for example. Diet doesn’t cause FPHL, but it does cause shedding which can make FPHL more obvious. The good news is, diet-related hair loss is usually reversible.
Marupatthu also tests for thyroid problems; both under and overactive thyroid conditions can affect hair growth. And she stresses that hair needs protein because that’s what it’s made from. The more you exercise, the more protein you need; heavy exercisers need a daily gram of protein per kilo of bodyweight.
Blood tests showed I was low in iron, the most common nutrient deficiency to impact hair, worsening with heavy periods in perimenopause. The normal level for ferritin (stored iron) starts at 41ng/mL, but to support hair growth it needs to be as high as 75ng/mL. My level was 12ng/mL and supplements barely shifted it, so I booked in for an iron transfusion procedure, which cost £770, at The Iron Clinic in London.
Other important hair nutrients are biotin, vitamin B2, zinc, selenium and vitamins A, C, D and E, says Morrell. However, it’s not clear how much a lack of each leads to hair loss.
Meshkati has formulated supplements to keep hair in its growing stage for longer, Hair Full Cycle. And the supplement most recommended by practitioners is Viviscal Professional.
Six months after the iron infusion, I noticed new baby hairs growing through. While the hair on my temples is staying stubbornly short, there is hair there so I’m no longer a candidate for a hair transplant. I still have bad hair moments, but if I can maintain my hair as it is now, I’ll feel I’ve got off lightly. If I can’t, I’ll have to accept it. As Jada Pinkett Smith posted on Instagram, “Me and this alopecia are going to be friends. Period”.
What women can do about midlife hair loss
The earlier you start treatment the better. Dermatologists and trichologists should consider all possible causes: nutrition, hormones, stress, medication, medical conditions.
Minoxidil is the first-line treatment – chemists sell it as Rogaine and other cheaper brands. It works for 60 to 70 per cent of women who have FPHL, but only while you’re using it.
Natural treatments that have some (limited) evidence are rosemary oil and pumpkin seed oil. And switch to low or no-chemical shampoo, conditioner and other products.
Taking HRT helps some women keep their hair. You could also try a topical lotion containing minoxidil, oestrogen and anti-androgens (philipkingsley.com).
Ask your GP to test your iron (ferritin), vitamin D and thyroid function. Try hair multivitamins, such as Viviscal Professional (available on prescription).
Massage helps increase blood flow to follicles; the website perfecthairhealth.com has a protocol you can follow (Founder Rob English is on YouTube). Red light treatment may also help increase blood flow to the scalp; the newest gadget is the CurrentBody Skin LED Hair Regrowth Device (£650 at currentbody.com). Microneedling with a roller or stamp (see weareplantmade.com) may also encourage growth.
Recommended
The 12 best treatments for thinning hair that actually work – for men and women


